High-speed fluid inside a pipeline acts like a sandblaster. It creates immense stress and erosion. If you choose the wrong pipe, you risk catastrophic leaks and expensive project shutdowns. The key to handling high-velocity flow lies in selecting seamless pipes with uniform structure and smooth internal surfaces. You must balance material hardness against corrosion resistance and calculate the correct wall thickness to withstand pressure spikes. This guide to choosing seamless steel pipe for high-velocity flow ensures your system remains safe and efficient for years.
I have seen many engineering projects fail because the purchasing team looked only at the price tag. They ignored the fluid speed. I want to share my experience so you can make the right choice.
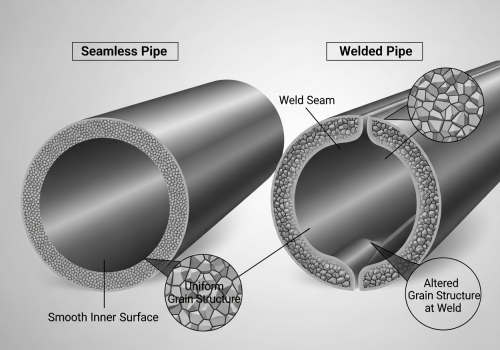
Welded seams are weak points. When fluid moves fast, it creates vibration and turbulence. These forces attack the weld, leading to cracks and sudden bursts that endanger your workers. Seamless pipes offer a continuous metal structure with no longitudinal welds. This homogeneity provides superior strength against the internal pressure fluctuations caused by high-velocity flow. They are the industry standard for critical safety applications in oil, gas, and power generation.

We need to look closely at the physics of flow to understand why seamless is better. When oil, gas, or steam moves at high speeds, it does not flow perfectly smooth. It creates turbulence. This turbulence hammers against the pipe wall. If there is a weld seam, that seam acts as a "speed bump." It disrupts the flow even more. This leads to localized erosion. Over time, the wall gets thinner right at the weld, creating a potential failure point. Seamless pipes do not have this problem. At Centerway Steel, we make pipes from solid billets. We heat a solid round bar and pierce it through the center. This means the grain structure of the steel is uniform all the way around. There is no weak side. This uniformity is critical when the fluid inside is moving at high velocity. For high-velocity flow, you also need to worry about pressure surges. If a valve closes quickly, the pressure spikes. This is called water hammer. A seamless pipe can stretch and absorb this shock much better than a welded pipe. If you are designing a system for a power plant or a refinery, you cannot take the risk with welded pipes in high-pressure lines. The seamless manufacturing process guarantees the reliability you need to sleep well at night.
Speed increases wear. If your fluid contains sand or particles, high velocity turns it into liquid sandpaper. The wrong material will wear out in months, forcing you to replace it. You must match the steel grade to the fluid type and speed. Carbon steel handles standard oil flow well. Alloy steels resist wear from particles. Stainless steel is essential when high velocity is combined with corrosive chemicals, as it maintains its protective layer better.

Choosing the material is perhaps the most complex part of the guide to choosing seamless steel pipe for high-velocity flow. You have to think about "erosion-corrosion." This happens when the fluid moves so fast that it strips away the protective oxide film inside the pipe. Once that film is gone, the bare metal eats away very fast. Here is a simple breakdown of how I look at materials based on my years at Centerway Steel:
| Material Type | Grade Examples | Best For | High-Velocity Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A106 Gr B, API 5L | General Oil & Gas | Good for clean fluids. High velocity can cause rapid erosion if particles are present. |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A335 P11, P22 | High Temp / Pressure | Harder material. Resists the physical scouring action of high-speed steam. |
| Stainless Steel | TP304, TP316 | Chemical / Corrosive | The best choice. The chromium creates a tough skin that high velocity finds hard to remove. |
If you are moving abrasive slurry, plain carbon steel is not enough. You need the hardness of alloy steel. If you are moving acidic gas at high speeds, you need stainless steel. I always tell my clients to analyze the medium first. Saving money on material now usually costs double in maintenance later. You must consider the hardness and the chemical composition together.
Many buyers guess the requirements. They copy specs from old projects. This is dangerous because every flow rate is different. You need a strict, step-by-step selection process. First, calculate your maximum flow velocity constraints using standards like API 14E. Next, determine the required wall thickness (Schedule) to handle the internal pressure. Finally, specify the surface finish, as a smoother bore reduces friction and turbulence in the system.
Let me walk you through the practical steps I use when helping a customer. This is the core of the guide to choosing seamless steel pipe for high-velocity flow.
Step 1: Velocity Limits. You cannot just push fluid as fast as you want. There is a limit. For liquids, we usually try to stay below 4.5 meters per second to stop erosion. For gases, it is much higher. You need to check the API 14E standard. It gives you the formula to find the erosional velocity limit. If you exceed this, no pipe will last.
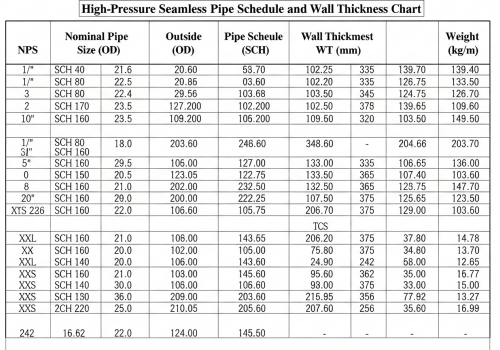
Step 2: Wall Thickness (Schedule). High velocity usually means high pressure. You need to pick the right Schedule (SCH 40, SCH 80, SCH 160). But here is the trick: if you pick a wall that is too thick, you reduce the inside diameter. A smaller inside diameter makes the fluid go even faster! It is a balancing act. You need a pipe strong enough for the pressure, but wide enough to keep the speed down.
Step 3: Surface Finish. This is often ignored. For high-velocity systems, I recommend Cold Drawn seamless pipes over Hot Rolled ones. Cold drawn pipes have a much smoother inside surface. A rough surface creates turbulence. Turbulence kills energy and damages the pipe. A smooth pipe lets the fluid glide.
Step 4: The Supplier. You must check the certifications. At Centerway Steel, we provide SGS and TUV inspection reports. When the flow is fast, the quality of the steel purity matters. Impurities in cheap steel will become pitting points for corrosion. You need a supplier who controls the entire process.
To safely manage high-speed fluids, you must prioritize seamless construction, select wear-resistant materials like alloy or stainless steel, and carefully calculate wall thickness. Following this guide to choosing seamless steel pipe for high-velocity flow ensures your project's safety and longevity.


