Are you worried about pipeline failures in your high-pressure projects? Choosing the wrong manufacturing method can lead to costly leaks. Here is how seamless pipes guarantee safety and durability. Seamless pipe is manufactured by heating a solid steel billet and piercing it through the center to create a hollow shell. This shell is then rolled, elongated, and sized to achieve precise dimensions. Unlike welded pipes, this process creates a uniform structure with no seams, offering superior strength for high-pressure applications.
Many people think all steel pipes are the same, but the way they are born changes everything. If you stop reading now, you might miss the critical differences between hot rolling and cold drawing that could save your project budget.
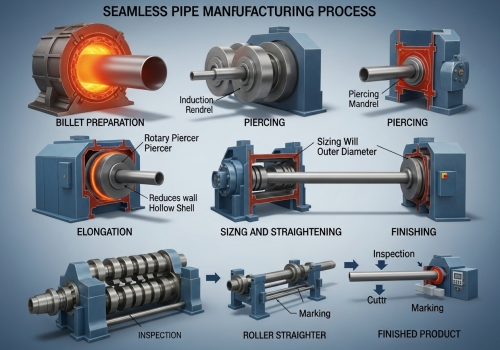
Most standard seamless pipes start in a furnace. If you do not understand this heating and piercing stage, you cannot judge the structural integrity of the final product. The hot rolling process begins by heating a solid steel billet to over 1,200°C. A piercing mill then pushes a mandrel through the soft steel to form a hollow shell. This method is fast and cost-effective for producing large diameter pipes with thick walls for general construction.

I remember a project where a client needed pipes for a thermal power plant. They were worried about the uniformity of the wall thickness because uneven walls can cause hotspots and rupture under high steam pressure. This is where understanding the hot rolling process helps you select the right grade. The process starts with a solid round steel billet. At Centerway Steel, we inspect this raw material carefully because any defect here will stretch out later in the process. First, we heat the billet in a rotary hearth furnace. The temperature must reach about 1,200°C. The steel becomes plastic and soft, glowing bright orange. Next is the most critical step, which we call the Mannesmann process. Two rollers spin the billet while a piercer point pushes into the center. It looks intense, like the steel is being turned inside out. This creates the "hollow shell." After piercing, the shell is thick and short. We must elongate it. We use a plug mill or a mandrel mill for this. The rollers reduce the wall thickness and increase the length significantly. Finally, the pipe passes through a sizing mill to ensure the outer diameter is exact. For standard sizes used in oil and gas transmission, this is the most common method. It provides a good balance of cost and speed while maintaining excellent structural integrity.
| Stage | Temperature | Purpose | Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating | ~1,200°C | Make steel malleable | Rotary Hearth Furnace |
| Piercing | High Heat | Create hollow shell | Piercing Mill (Mannesmann) |
| Rolling | Dropping | Reduce wall thickness | Mandrel Mill / Plug Mill |
| Sizing | Cooling | Fix outer diameter | Sizing Mill |
Hot rolled pipes are great, but they lack the extreme precision some German engineers demand. If your project requires tight tolerances, you need to look at the cold drawing method. Cold drawing is a secondary process performed after hot rolling to increase precision and surface quality. The pipe is pulled through a die at room temperature to reduce its diameter and wall thickness. This method produces pipes with smoother surfaces, higher yield strength, and very tight dimensional tolerances.

| Feature | Hot Rolled Seamless | Cold Drawn Seamless |
|---|---|---|
| Production Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Surface Finish | Rough, oxide scale present | Smooth, shiny |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Moderate | High (Tight Tolerances) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Use | Oil Pipelines, Structure | Hydraulics, Automotive |
Manufacturing the pipe is only half the battle. If you do not verify the integrity of the steel, you are risking a catastrophic failure in the field. Quality control for seamless pipes involves both destructive and non-destructive testing. We use Ultrasonic Testing (UT) to find internal cracks and Hydrostatic Testing to ensure the pipe can hold pressure. These tests verify that the finished product meets international standards like API 5L and ASTM A106 before shipment.

At Centerway Steel, we know that a piece of paper saying "certified" is not enough. You need proof. I once had a customer who bought cheap pipes elsewhere to save money, and they burst during a pressure test at the site. It cost them millions in delays. That is why testing is non-negotiable for us. We start with Visual Inspection. We check for surface marks, straightness, and end bevels. But eyes cannot see inside the steel. So, we use Ultrasonic Testing (UT). Sound waves travel through the metal. If they hit a crack or an air pocket, the machine alerts us immediately. This is vital for high-pressure gas lines where a hidden flaw could be deadly. We also perform Hydrostatic Testing on every single pipe. We fill the pipe with water and pressurize it higher than its operating limit for a set time. If it leaks or deforms, it is rejected. We also do chemical analysis to ensure the mix of carbon and alloys is correct. We follow standards like ASTM and API strictness. For an EPC manager, these reports are your insurance policy. They prove the pipe will last for 20 or 30 years.
· Hydrostatic Testing: Verifies pressure capability and leak tightness.
· Eddy Current Testing: Finds surface defects and cracks.
· Impact Testing (Charpy V-Notch): Checks toughness at low temperatures to prevent brittle fracture.
Here are the most common questions our clients ask when selecting between seamless and welded options.
Q: Are seamless pipes stronger than welded pipes?
A: Yes, generally speaking. Seamless pipes have no welded seams, which are often considered the "weak link" in a pipe's structure. This homogeneous structure allows them to withstand roughly 20% higher working pressures than welded pipes of the same size and grade, making them the standard choice for critical oil and gas applications.
Q: Can seamless pipes be customized in size?
A: Absolutely. While hot-rolled pipes come in standard sizes (like 2-inch, 4-inch), we can use the cold drawing process mentioned above to achieve non-standard diameters and specific wall thicknesses. This is essential for custom machinery or retrofitting old equipment where standard off-the-shelf sizes do not fit.
Q: What is the maximum temperature seamless pipes can withstand?
A: This depends entirely on the material composition rather than the manufacturing method alone. Standard carbon steel seamless pipes can handle up to 425°C (800°F). However, if we manufacture the pipe using alloy steel (adding chromium or molybdenum), it can withstand temperatures up to 600°C (1,112°F) or even higher for specialized boiler tubes.
Q: How are seamless pipes tested for defects?
A: We use a multi-layered approach. Beyond visual inspection, we utilize Ultrasonic Testing (UT) to see inside the steel walls and Hydrostatic Testing to physically test pressure limits. Eddy Current testing is also used for surface defect detection. All tests are documented in the Mill Test Certificate (MTC) provided with the shipment.
Seamless pipes are made through heating, piercing, and rolling to ensure uniform strength. For high-pressure projects, choosing the right production method—whether hot rolled for bulk efficiency or cold drawn for precision—is critical. Verifying quality with a partner like Centerway Steel guarantees safety and performance for your project.


